XpertDox Team
The healthcare industry is experiencing a significant transformation, moving away from the traditional fee-for-service model and toward value-based care, which prioritizes quality and cost-effectiveness. Accurate risk adjustment is crucial to the success of value-based care, with Hierarchical Condition Category (HCC) coding playing a central role. However, relying on traditional, manual methods for achieving accurate HCC coding presents considerable challenges.
The large volume of patient data, the complexity of medical documentation, and the constantly changing coding guidelines can lead to errors and inefficiencies. Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers a solution to these challenges. This blog explores how AI is revolutionizing HCC coding by increasing accuracy, enhancing compliance, and ultimately supporting improved patient care within the value-based care framework.
Value-Based Care: A New Healthcare Approach
The way healthcare is delivered and paid for is changing. Traditionally, the system has operated under a fee-for-service model. In this model, healthcare providers such as doctors and hospitals are paid for each individual service they provide, including tests, procedures, and visits. This approach emphasizes the volume of services delivered.
Value-based care represents a shift from this model. Rather than focusing on the quantity of services, it prioritizes the value of care. In value-based care, value is defined as achieving positive health outcomes for patients at a reasonable cost. Essentially, it's a system that rewards quality and results, not just the volume of care provided.
Core Ideas Behind Value-Based Care:
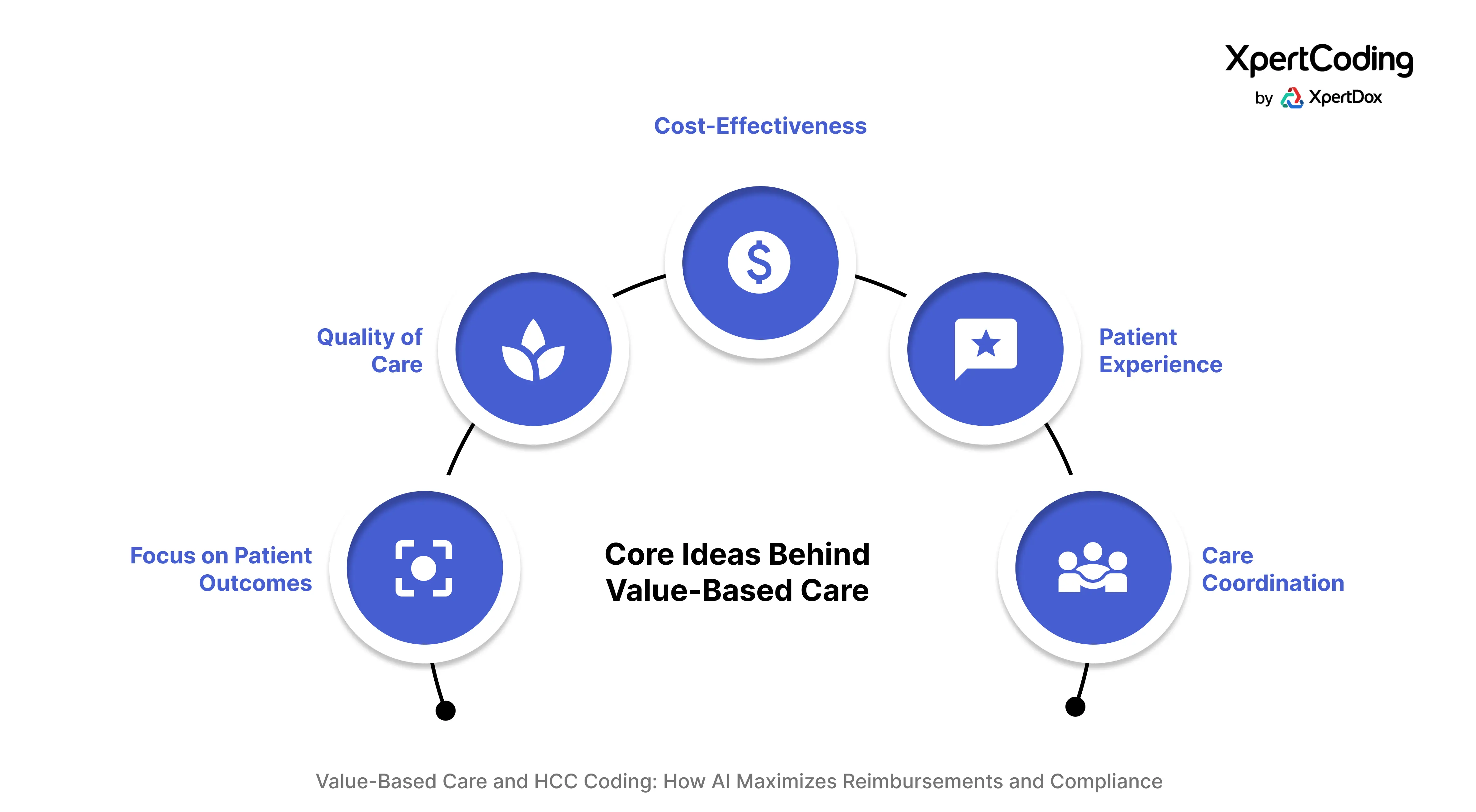
Value-based care is guided by several core principles:
- Improved Patient Outcomes: The primary focus is on enhancing patients' health and well-being.
- Enhanced Quality of Care: Delivering the highest possible care based on evidence-based practices.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Managing and reducing unnecessary healthcare expenses.
- Positive Patient Experience: Ensuring patients are satisfied with their care and feel supported throughout their healthcare journey.
- Care Coordination: Facilitating seamless and comprehensive care through effective collaboration among healthcare providers.
Drivers of the Shift to Value-Based Care
Several factors are driving the transition to value-based care:
- Rising Healthcare Costs: The continuous increase in healthcare costs necessitates a focus on cost containment.
- Emphasis on Proactive Health: There's a growing recognition that focusing on preventive care and overall wellness is essential, not just treating illnesses.
- Demand for Patient-Centered Care: Patients expect care that is tailored to their individual needs and delivers optimal outcomes.
- Inefficiencies of Fee-for-Service: The fee-for-service model can incentivize unnecessary tests and procedures, which do not always translate to improved health.
Value-Based Care Models
Value-based care is implemented through various models, including:
- Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs): ACOs are groups of doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare providers who collaborate to coordinate care for their patients. These organizations may share in cost savings if they deliver high-quality care and effectively manage costs.
- Bundled Payments: In this model, a single, predetermined payment covers all services related to a specific treatment episode (e.g., surgery), encouraging providers to work together efficiently.
- Capitation: Providers receive a fixed payment per patient over a specific period, regardless of the volume of services provided, incentivizing a focus on patient health maintenance.
- Pay-for-Performance: Providers receive financial incentives for meeting specific quality and performance targets, such as patient satisfaction or effective management of chronic conditions.
Value-based care aims to create a more sustainable and patient-centered healthcare system by rewarding quality and positive health outcomes.
Advanced AI-powered technologies like XpertCoding can significantly improve care coordination and collaboration across healthcare teams.
Understanding the Role of HCC Coding in Value-Based Care
Hierarchical Condition Category (HCC) coding is a system that categorizes patients' health status based on their medical diagnoses. This system translates the detailed information about a patient's health conditions, as documented by healthcare providers, into a standardized set of codes. These codes provide a framework for understanding the complexity of a patient's health profile.
At its core, HCC coding utilizes the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) codes assigned by healthcare professionals to describe illnesses and conditions. However, it's important to note that not all ICD-10-CM codes are HCC codes. Only specific ICD-10-CM codes are mapped to particular HCC categories.
The Hierarchical Structure of HCCs
A key feature of the HCC system is its hierarchical structure. When a patient has multiple related health conditions, the HCC system recognizes and prioritizes the most severe or complex condition. This hierarchical approach ensures that the risk assessment accurately reflects the patient's highest level of illness burden.
- Hierarchical Structure: More severe conditions take precedence over less severe related conditions.
- Example: A patient diagnosed with both uncomplicated diabetes and diabetes with chronic kidney disease will be assigned the HCC for diabetes with chronic kidney disease.
- Benefit: This prevents overcounting of related conditions and ensures accurate representation of the patient's overall health complexity.
Risk Adjustment in Value-Based Care
Value-based care emphasizes quality and effectiveness, making it essential to ensure fair and equitable payments to healthcare providers and plans. Recognizing that different patient populations have varying health needs and that caring for patients with greater health challenges often requires more resources, risk adjustment plays a crucial role.
- Adjust Payments: Risk adjustment facilitates the adjustment of payments to healthcare providers based on the health status of their patient population.
- Fair Reimbursement for Complex Cases: Without risk adjustment, providers who care for a higher proportion of patients with chronic or severe conditions may face financial disadvantages or appear to have lower quality outcomes, simply due to the inherent complexity of treating those patients.
HCC and Risk Scores
HCC coding is a fundamental component of many risk adjustment models. Risk scores, calculated based on the HCC codes assigned to a patient, provide a numerical representation of the predicted cost of caring for that patient relative to the average patient. Patients with a greater number and severity of HCCs will have higher risk scores, indicating a higher expected cost of care.
- Healthcare providers and plans utilize these risk scores to adjust payments.
- Example: Medicare Advantage plans receive higher payments for enrollees with higher risk scores, acknowledging the increased resources required for their care.
- Goal: To ensure fair compensation for managing patients with complex health needs.
- Impact: To support the delivery of high-quality care within value-based care frameworks.
Importance of HCC Coding in Value-Based Care
By providing a standardized methodology to categorize patient health status based on chronic conditions, HCC coding is crucial for ensuring fair reimbursement and effective risk management within value-based care frameworks. Its importance is highlighted by the following key aspects:
- Facilitates Fair Risk Adjustment: HCC coding provides the essential data for risk adjustment, ensuring that healthcare providers and plans receive equitable compensation that accurately reflects the health burden of their patient populations. This prevents providers caring for more complex patients from being unfairly penalized financially.
- Enables Accurate Payment Models: By quantifying patient complexity through HCCs and subsequent risk scores, value-based care models can develop more accurate and equitable payment structures. This ensures appropriate resource allocation based on the anticipated healthcare needs of different patient groups.
- Supports Quality Improvement Initiatives: The detailed patient data captured through HCC coding offers valuable insights into the prevalence of chronic conditions within a patient population. This information can be leveraged to inform and target quality improvement initiatives aimed at effectively managing these conditions.
- Drives Comprehensive Documentation: The requirement for accurate HCC coding incentivizes healthcare providers to ensure thorough and specific documentation of all relevant chronic conditions. This emphasis on comprehensive documentation not only supports accurate coding but also contributes to enhanced overall patient care and communication among providers.
- Contributes to Meaningful Performance Measurement: In value-based care, performance is often evaluated based on outcomes and cost-efficiency. Accurate risk adjustment, facilitated by HCC coding, ensures that performance metrics are not skewed by variations in patient health complexity, enabling more meaningful comparisons and evaluations of care delivery effectiveness.
XpertDox’s autonomous medical coding platform is compatible with leading EHR systems, ensuring smooth workflow and enhanced coding processes!
Challenges of Traditional HCC Coding
While HCC coding is essential for the success of value-based care, relying solely on traditional, manual methods presents significant challenges for healthcare organizations. These challenges can negatively affect accuracy, efficiency, compliance, and the financial integrity of value-based care initiatives.
1. The Complexity of Medical Documentation
The sheer volume of patient data generated within contemporary healthcare systems poses a substantial obstacle for manual HCC coding. Coders are required to review extensive electronic health records (EHRs), physician notes, laboratory results, and other clinical documents for each patient.
- Vast Amounts of Data: The sheer quantity of information makes thorough manual review time-consuming and demanding.
- Fragmented Documentation: Patient information is often dispersed across various systems and generated by multiple providers in different locations. This lack of a unified view hinders the ability to obtain a comprehensive understanding of a patient's health history.
- Identifying Relevant Conditions: Locating all chronic conditions that qualify for HCC coding within lengthy and often unstructured physician notes can be challenging. Coders may overlook subtle mentions or conditions not explicitly addressed during a particular encounter.
2. The Burden of Manual Chart Review and Abstraction
Manually reviewing patient charts and abstracting the necessary information for HCC coding is inherently labor-intensive and susceptible to human error.
- Time-Consuming Process: Coders must dedicate significant time to thoroughly reviewing each patient chart, interpreting the clinical context, and identifying all applicable HCC codes.
- Potential for Human Error: Despite the expertise of certified coders, the manual nature of this work elevates the risk of errors, including missed conditions, incorrect code assignments, and misinterpretations of clinical language.
- Coder Fatigue: The repetitive and detail-oriented nature of manual chart review can contribute to coder fatigue, further increasing the likelihood of errors and reducing efficiency.
- Variability in Interpretation: Different coders may interpret the same clinical documentation differently, leading to inconsistencies in HCC assignments across the organization.
3. Keeping Pace with Evolving Guidelines and Regulations
The landscape of HCC coding is dynamic, with coding guidelines, payer rules, and regulatory requirements subject to frequent updates and changes. This dynamic environment presents an ongoing challenge for coding teams.
- Frequent Updates: Staying informed about the latest changes to HCC coding rules, ICD-10-CM guidelines, and payer-specific policies demands continuous effort and resources.
- Ensuring Consistent Application: Even when coders are aware of updates, ensuring their consistent application across all coding staff can be difficult, potentially resulting in inconsistencies in coding practices.
- Risk of Non-Compliance: Failure to adhere to the latest guidelines can lead to non-compliance, exposing the healthcare organization to potential penalties, audits, and financial repercussions.
- Resource-Intensive Training: Maintaining up-to-date knowledge among coding teams necessitates a substantial investment in training, education, and access to current resources.
4. Ensuring Comprehensive and Accurate Capture of Chronic Conditions
A fundamental goal of HCC coding is to capture a complete and accurate representation of a patient's chronic health conditions. However, traditional methods often struggle to achieve this.
- Difficulty Capturing All Eligible Conditions: Some chronic conditions may not be actively managed or explicitly documented in every patient encounter, making them susceptible to being missed during manual review.
- Importance of Documentation Specificity: Accurate HCC assignment often depends on the specificity of the documentation. Vague or incomplete documentation can hinder the assignment of the most appropriate and specific HCC codes.
- Potential for Undercoding: These challenges create a significant risk of undercoding, where eligible HCC conditions are not identified and coded. This leads to an underestimation of the patient's risk score and, consequently, under-reimbursement for the care provided.
These challenges inherent in traditional HCC coding underscore the need for more advanced and efficient solutions to ensure accuracy, optimize workflows, and maximize the benefits of risk adjustment in value-based care.
If you’re tired of slow, manual HCC coding, it’s time to make a switch! See how XpertDox automates the process to achieve faster and more accurate results.
Transforming HCC Coding in Value-Based Care with AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is emerging as a powerful tool to address the significant challenges associated with traditional HCC coding. By leveraging advanced algorithms and computational power, AI can revolutionize the HCC coding, leading to greater accuracy, improved compliance, and optimized reimbursements within value-based care frameworks.
1. Enhances Accuracy in HCC Coding
AI algorithms, particularly those utilizing Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML), offer exceptional capabilities for analyzing the substantial volumes of unstructured clinical data found in electronic health records (EHRs).
- Efficient and Accurate Data Analysis: AI can rapidly process and analyze extensive collections of patient documents, including physician notes, discharge summaries, and radiology reports. Its capacity to consistently scan and interpret large volumes of text significantly improves the efficiency of data review.
- Identifying Key Medical Entities and Understanding Context: NLP techniques enable AI to understand the nuances of clinical language, including diagnoses, procedures, medications, and symptoms. Furthermore, AI can analyze the context in which these elements are mentioned, discerning their relationships and relevance to a patient's chronic conditions, thereby facilitating accurate HCC assignment.
- Detecting Indirectly Mentioned Conditions: AI can identify chronic conditions that are not explicitly documented as active diagnoses in a particular encounter. By analyzing a patient's complete record, AI can recognize patterns, past diagnoses, and mentions of ongoing health issues that may be relevant for HCC coding but easily overlooked in a manual chart review.
- Uncovering Subtle Indicators of HCC-Eligible Conditions: AI algorithms can detect subtle linguistic cues and patterns in clinical text that may indicate the presence of an HCC-eligible condition. AI can identify phrases describing the management of a specific chronic illness, even without a formal diagnosis explicitly stated in a current note. Similarly, AI can flag mentions of complications or manifestations of a known chronic condition, ensuring a more comprehensive capture of the patient's health burden.
2. Boosts Efficiency and Reduces Administrative Burden
The application of AI to HCC coding yields significant efficiency gains and a substantial reduction in the administrative burden associated with manual processes.
- Automated Chart Review and Abstraction: AI can automate the time-consuming tasks of reviewing patient charts and extracting the pertinent information required for HCC coding. This frees up coders from repetitive manual tasks, enabling them to concentrate on more complex cases.
- Prioritization of Charts for HCC Opportunities: AI algorithms can analyze patient data and prioritize charts that are more likely to contain undocumented or undercoded HCC-eligible conditions. This empowers coding teams to focus their review efforts and optimize coding accuracy and reimbursement.
- Reduction in Manual Errors and Streamlined Workflows: By automating significant portions of the HCC coding process, AI inherently reduces the potential for human errors, such as missed conditions or incorrect code assignments. This results in more efficient and reliable coding workflows, enhancing overall productivity and data quality.
- Integration with EHRs for Real-Time Insights: Advanced AI-powered HCC coding solutions can be integrated with existing Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems. This integration enables AI to provide real-time coding suggestions to clinicians during the documentation process and perform validation checks on assigned codes. This proactive approach can improve the accuracy and completeness of documentation at the point of care, further optimizing the efficiency and effectiveness of HCC coding.
3. Ensures Compliance and Stays Updated
In the evolving healthcare landscape, maintaining compliance with HCC coding guidelines and payer rules is a continuous challenge. AI offers robust tools to address these complexities.
- Continuous Updates with Latest Guidelines and Regulations: Leading AI-powered HCC coding systems are continuously updated with the latest HCC coding guidelines, ICD-10-CM updates, official coding advice, and payer-specific policies. This ensures that the AI algorithms utilize the most current information, mitigating the risk of coding errors due to outdated knowledge.
- Flagging Potential Compliance Risks and Inconsistencies: AI can identify potential compliance risks and inconsistencies in coding practices across an organization. For example, it can flag instances where coding patterns deviate from established guidelines or documentation may not adequately support the assigned HCC codes. Identifying potential issues early allows for timely review and correction, minimizing the risk of audit findings and penalties.
- Providing Audit Trails and Documentation to Support Coding Decisions: AI-powered HCC coding platforms often maintain comprehensive audit trails that document the AI's analysis and the rationale behind its coding suggestions. This detailed documentation is invaluable during internal and external audits, providing transparency and supporting the coding decisions made by both AI and human coders. The availability of this information streamlines the audit process and provides evidence of compliance efforts.
4. Maximizing Reimbursements Through Comprehensive HCC Capture
Ultimately, the accurate and efficient application of HCC coding directly impacts the financial health of healthcare organizations participating in value-based care models. AI maximizes reimbursements by enabling a more comprehensive capture of eligible chronic conditions.
- Identifying a Wider Range of Eligible Chronic Conditions: AI's ability to analyze large volumes of unstructured data and identify both direct and indirect mentions of chronic conditions leads to a more complete capture of a patient's health burden. This broader identification of HCC-eligible conditions results in a more accurate representation of patient risk.
- Leading to More Accurate Risk Scores: By capturing a more comprehensive set of HCCs, AI facilitates the calculation of more accurate risk scores. These scores provide a more precise reflection of the true complexity and anticipated healthcare resource utilization of the patient population.
- Translating to Maximized Reimbursements: In value-based care models that utilize risk-adjusted payments, more accurate risk scores directly translate into optimized reimbursements for the healthcare organization. This ensures that providers are fairly compensated for the care they deliver to their patients, particularly those with complex chronic conditions.
- Reducing Undercoding and Ensuring Fair Compensation: AI reduces the risk of undercoding. By ensuring that all eligible HCCs are captured and coded, AI helps healthcare organizations receive the appropriate level of reimbursement, leading to fair compensation for the care provided to patients with complex needs and supporting the financial stability of their participation in value-based care programs.
Do you want to capture all the reimbursements you deserve? Learn how XpertCoding’s Business Intelligence platform offers valid insights to improve your coding accuracy and operational efficiency!
Implementing AI for HCC Coding
The decision to integrate Artificial Intelligence into your HCC coding workflow is significant and offers substantial potential for improved accuracy and efficiency. However, successful implementation necessitates careful consideration of several key factors and adherence to best practices. A strategic approach to this transition will ensure a smooth integration and maximize the benefits of AI for your organization.
1. Choosing the Right AI Solution for Your Organization
Selecting the appropriate AI-powered HCC coding platform is a critical initial step. Several factors require careful evaluation to ensure the chosen solution aligns with your organization's specific needs and infrastructure.
- Accuracy Rates: Investigate the AI platform's demonstrated accuracy through rigorous testing and validation. Prioritize solutions with a proven track record of high precision in HCC identification and coding.
- Integration Capabilities: Verify the platform's ability to seamlessly integrate with your existing Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems, coding platforms, and other relevant healthcare IT tools. Seamless data exchange is crucial for an efficient workflow.
- Vendor Support: Assess the level of support provided by the vendor, including implementation assistance, technical support, ongoing maintenance, and training resources. A reliable and responsive vendor is essential for a successful partnership.
- Scalability: Consider the platform's ability to scale as your organization's needs evolve and patient volumes change. The AI solution should adapt to future growth.
- Security: Scrutinize the vendor's security protocols and compliance measures to protect sensitive patient data. Adherence to regulations such as HIPAA is essential.
- Transparency and Explainability: Seek to understand how the AI model arrives at its coding suggestions. While the underlying mechanisms may be complex, transparency and explainability can foster trust and facilitate human validation. Understanding the factors the AI considers can aid in interpreting its recommendations.
2. Seamless Integration with Existing Healthcare IT Infrastructure
AI must integrate smoothly with your current technology ecosystem to function effectively within your HCC coding processes.
- EHR System Compatibility: The AI platform should readily connect with your primary EHR system to access patient data without requiring cumbersome manual data transfers.
- Interoperability: Ensure the AI solution can effectively interact with your organization's other coding platforms, data analytics tools, and reporting systems. Seamless data flow between these systems is key to a holistic approach to revenue cycle management.
- Ease of Use: The implementation of AI systems should minimize disruption to existing workflows and be user-friendly for coders and clinicians. A well-integrated system should enhance, not hinder, daily operations.
3. The Crucial Role of Human Oversight and Validation
While AI can transform HCC coding, it's essential to recognize that it's a powerful tool that enhances, rather than replaces, human expertise.
- AI as an Augment, Not a Replacement: Qualified and experienced medical coders remain vital to the HCC coding process. AI can handle the initial data analysis and code suggestions, but human judgment is crucial for complex cases and final validation.
- Review and Validation of AI Suggestions: Coders should review the codes suggested by the AI platform to ensure accuracy, particularly in nuanced or ambiguous clinical scenarios. Human expertise can identify potential edge cases or contextual information that the AI might not fully comprehend.
- Handling Complex Cases: Certain complex medical situations or poorly documented cases may require a human coder's critical thinking and clinical knowledge to determine the most accurate HCC assignments.
- Collaborative Approach: Fostering a collaborative environment where AI and human coders work together is key to maximizing efficiency and accuracy. AI can manage volume and initial identification, while human coders provide oversight and expertise.
4. Training and Change Management for Coding Teams
The successful adoption of AI in HCC coding necessitates adequate training for your coding staff and a well-managed change process.
- Comprehensive Training: Provide thorough training to your coding team on how to use and interact with the new AI platform. This training should cover the system's features, workflows, and how to review and validate AI-suggested codes.
- Addressing Concerns and Fostering Buy-in: Acknowledge that introducing AI may generate concerns among coding staff. Proactively address these concerns, communicate the benefits of AI in augmenting their work, and emphasize the opportunity for them to focus on more complex and strategic tasks.
- Phased Implementation: Consider a phased rollout of the AI platform, beginning with specific departments or workflows, to facilitate gradual adaptation to the new technology.
- Ongoing Support and Feedback Mechanisms: Provide ongoing support to your coding team as they integrate AI into their workflows. Establish channels for feedback to identify any challenges and areas for improvement in the implementation process.
5. Data Security, Privacy, and Compliance
The security and privacy of sensitive patient health information (PHI) must be paramount when implementing AI for HCC coding.
- Adherence to HIPAA and Privacy Regulations: Ensure that the chosen AI vendor and platform fully comply with all relevant data security and privacy regulations, including HIPAA in the United States.
- Robust Security Measures: Inquire about the specific security measures implemented by the vendor to protect patient data, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
- Vendor Certifications: Prioritize vendors with relevant security certifications that demonstrate their commitment to protecting sensitive information.
- Data Governance Policies: Establish clear data governance policies within your organization regarding the access, use, and storage of patient data processed by the AI system.
By thoughtfully addressing these key considerations and implementing best practices, your healthcare organization can effectively leverage the power of AI to transform your HCC coding processes.
Are you looking for the right AI-powered coding solution that prioritizes security and compliance? Discover how XpertDox helps safeguard your client’s information.
The Future of AI in HCC Coding and Value-Based Care
The integration of Artificial Intelligence into HCC coding is not a static event but rather the beginning of a continuous evolution. As AI algorithms and capabilities advance, their impact on HCC coding and the broader landscape of value-based care is poised to become even more significant.
Continuous Evolution of AI Algorithms and Capabilities
The fields of AI, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Machine Learning (ML) are experiencing rapid advancements. These ongoing developments hold the promise of further enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of AI-powered HCC coding solutions.
- Enhanced Accuracy and Efficiency: Future iterations of AI algorithms will likely demonstrate even greater sophistication in understanding clinical context, identifying subtle nuances in medical language, and accurately assigning HCC codes. Continuous learning from extensive datasets will refine their ability to minimize errors and process information with increasing speed.
- Predicting Future Risk: The analytical capabilities of AI have the potential to move beyond simply identifying current chronic conditions to predicting future health risks for patients. AI could help identify patients at high risk of developing specific conditions by analyzing historical data, genetic information, and other relevant factors. This predictive capability can inform proactive care management strategies and potentially prevent or mitigate future health issues.
- Identifying Emerging Health Trends: AI may also facilitate the identification of emerging health trends and patterns within populations by continuously monitoring and analyzing large-scale patient data. This information could be valuable for public health initiatives, resource allocation, and the early detection of potential health crises.
Deeper Integration with Clinical Workflows
The future likely involves a deeper integration of AI-powered risk adjustment insights directly into healthcare providers' clinical workflows.
- Real-Time Risk Adjustment Insights for Clinicians: Imagine a scenario where AI provides clinicians with real-time feedback during patient encounters, highlighting potential HCC-eligible conditions based on their documentation. This immediate feedback can prompt more comprehensive and specific documentation at the point of care.
- More Comprehensive Documentation: By providing timely reminders and suggestions, AI can encourage clinicians to document all relevant chronic conditions with the level of detail required for accurate HCC coding. This can lead to a more complete and accurate representation of the patient's health status.
- Proactive Care Management: The insights generated by AI, including potential future risks, can empower clinicians to develop more proactive and personalized care management plans. By identifying patients who may benefit from early interventions or targeted therapies, AI can improve patient outcomes and potentially reduce the overall cost of care.
Expanding Applications of AI in Risk Adjustment and Value-Based Care
While HCC coding has a significant impact, AI applications in risk adjustment and value-based care are likely to expand beyond this specific model.
- Application to Other Risk Adjustment Models: The principles and techniques employed by AI in HCC coding could be adapted and applied to other risk adjustment methodologies used in various value-based care programs. This could lead to broader improvements in the accuracy and efficiency of risk adjustment across different payment models.
- Supporting Population Health Management: AI's ability to analyze large datasets and identify patterns can be a powerful tool for population health management initiatives. It can help identify high-risk individuals within a population, track the prevalence of certain conditions, and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions at a population level.
- Enhancing Quality-Improvement Efforts: AI-generated data insights can also be leveraged to support quality-improvement efforts within healthcare organizations. By identifying areas where documentation or coding practices could be improved, AI can contribute to enhanced data quality and more accurate performance measurement.
Conclusion
The transition to value-based care necessitates a sophisticated understanding of patient health, and accurate HCC coding is a cornerstone of this evolution. Artificial Intelligence overcomes the limitations of traditional methods and offers a powerful and transformative solution. Beyond incremental improvements, AI optimizes reimbursements and compliance in HCC coding. The future of successful value-based care relies on embracing these intelligent tools to ensure fair reimbursement and, ultimately, drive improved outcomes for patients.
Are you ready to experience the transformative power of AI in your HCC coding processes? XpertCoding is a cutting-edge, automated, AI-powered coding platform designed to streamline workflows, enhance accuracy, and maximize your success in value-based care.
Don't let manual processes hold you back. Contact XpertDox today for a personalized free demo and take the first step towards a smarter, more efficient future for your HCC coding efforts!
Published on - 04/05/2025








